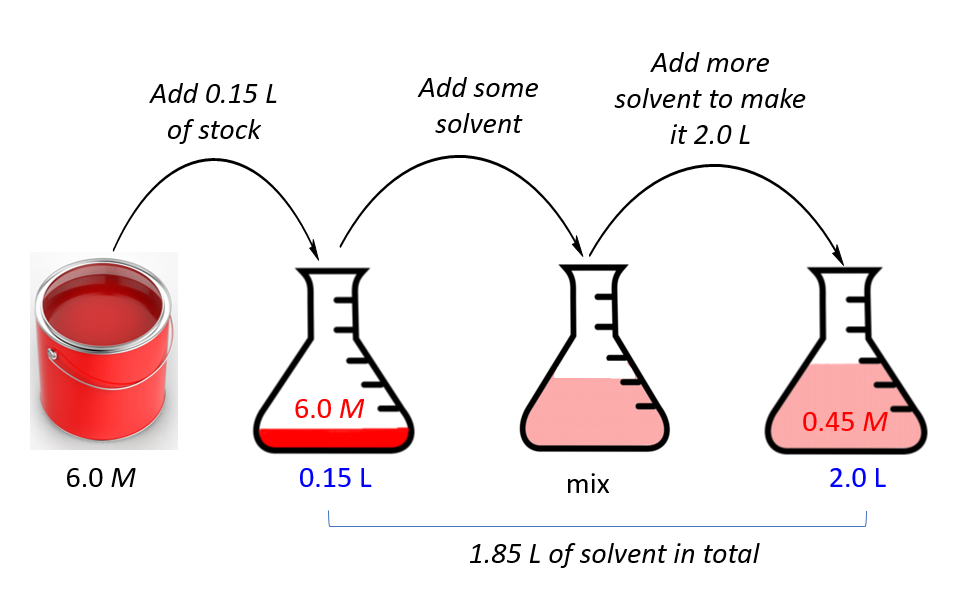
Dilution Equation In Chemistry . Using the dilution equation, we write: Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. We are often concerned with. The volumes must be expressed in the same units. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Often, a worker will need to change the concentration of a solution by changing the. (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100.
from general.chemistrysteps.com
The volumes must be expressed in the same units. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. We are often concerned with. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. Using the dilution equation, we write: Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory.
Dilution of a Stock Solution and Calculations Based Morality
Dilution Equation In Chemistry Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. Using the dilution equation, we write: We are often concerned with. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. Often, a worker will need to change the concentration of a solution by changing the. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. The volumes must be expressed in the same units. (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Analytical Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Dilution Equation In Chemistry Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. The volumes must be expressed in the same units. Notice that the. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
A Level Chemistry Dilution Calculations Worked Example YouTube Dilution Equation In Chemistry Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. Often, a worker will need to change the concentration of a solution by changing the. Understand how stock solutions are used in. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From general.chemistrysteps.com
Dilution of a Stock Solution and Calculations Based Morality Dilution Equation In Chemistry A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. We are often concerned with. Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. Using the dilution equation,. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
TRU Chemistry Labs How To do Dilution Calculations YouTube Dilution Equation In Chemistry Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. The volumes must be expressed in the same units. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. Using the dilution equation, we write: Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Apply the dilution equation to calculate. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
What Is Dilution? Chemistry Matters YouTube Dilution Equation In Chemistry The volumes must be expressed in the same units. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. Using the dilution equation, we write: A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Learn how to dilute. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Chem 11 Dilution Calculations_Solving for Final Volume after Dilution Dilution Equation In Chemistry (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. A more simplified way of. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From labpedia.net
Solutions Part 1 Solutions Preparation used in Clinical Laboratory Dilution Equation In Chemistry Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. We are often concerned with. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. A more simplified way. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Dilution Calculations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Dilution Equation In Chemistry A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. We are often concerned with. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. Often, a worker will need to change the concentration of a solution. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Calculating Dilution Factor YouTube Dilution Equation In Chemistry (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. Note. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Making Molar Solutions PowerPoint Presentation, free download Dilution Equation In Chemistry Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. We are often concerned with. Often, a worker will need to change the concentration of a solution by changing the. Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. Using the dilution equation, we write:. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.madebyteachers.com
Dilution, Molarity, and Volume Calculations A Chemistry Worksheet Dilution Equation In Chemistry Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. The volumes must be expressed in the same units. Often, a worker will need to change the concentration of a solution by changing the. (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory.. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From chem.libretexts.org
5.2 Solutions and Dilutions Chemistry LibreTexts Dilution Equation In Chemistry A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. The volumes must be expressed in the same units. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. Note that this equation. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Serial Dilution Method Protocol Step Wise Explanation YouTube Dilution Equation In Chemistry A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. (m1) (v1). Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From kayliefernandez.blogspot.com
PreAP Chemistry Dilutions Dilution Equation In Chemistry Using the dilution equation, we write: (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. We are often concerned with. Often, a worker. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
Dilution and Dilution Factor in Microbiology How to Calculate Dilution Equation In Chemistry Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. A more simplified way of solving this is by using the dilution formula: Often, a worker will need to change the concentration of a solution by changing the. Using the. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From cfmuvi.jimdo.com
Simple Serial Dilution Calculation cfmuvi Dilution Equation In Chemistry Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Explain how concentrations can be changed in the lab. Notice that the volumes need not be converted to.. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.ck12.org
Dilution (M[i]V[i]=M[f]V[f]) Example 1 ( Video ) Chemistry CK12 Dilution Equation In Chemistry Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Using the dilution equation, we write: Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. (m1) (v1) = (m2) (v2), where m's are molarities and v's are. (1.50 mol/l) (53.4 ml) = (0.800 mol/l) (x) x = 100. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. A more simplified way of. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.
From www.expii.com
Dilution of Solutions — Overview & Examples Expii Dilution Equation In Chemistry Note that this equation gives only the initial and final. Understand how stock solutions are used in the laboratory. We are often concerned with. Learn how to dilute and concentrate solutions. Apply the dilution equation to calculate the final concentration, or the final volume, of a diluted. Often, a worker will need to change the concentration of a solution by. Dilution Equation In Chemistry.